springmvc的配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 默认加载的springmvc的配置文件时在 WEB-INF下的spring-servlet.xml
init-param指定springmvc的配置文件的位置
-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- 在web服务器启动的时候就加载DispatcherServlet,可以减少用户第一次请求的时间 -->
<load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>RequestMapping
Ant风格的value(value是字符串数组,可以填写多个路径)
使用
@RequestMapping("/test")时,value字符串的值可以是?、*、**? 代表任意
1个字符* 代表0-N个任意字符
** 代表0-N个任意字符,并且路径中可以出现路径分隔符
/注意** 在使用的时候,如果左右有字符,其效果和* 没区别,
在spring6中 “/**/xxx” 不允许这样,会报错,spring5不会
因此在spring6中** 通配符只能作为路径的末尾 “/xxx/**”
method 属性
限制允许的请求方法
路径参数 @PathVariable
// 路径参数
// http://localhost:8080/springmvc/login/zwc/123
@RequestMapping("/login/{username}/{password}")
public String login(
// @PathVariable注解 指定路径参数
@PathVariable("username") String username,
@PathVariable("password") String password
) {
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
return "ok";
}RequestParam 请求参数
若参数与指定的参数名或者参数值不对,则会返回400
使用@RequestParam 获取到请求参数

// params用来限制请求中的参数,具体的用法见上图。 下面的请求参数中必须包含username和password
// get是queryString中包含参数
// post是请求体中包含 参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParams", method = RequestMethod.POST, params = {"username", "password"})
public String testParams(
//这三个参数tomcat会自动传过来,直接使用即可
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
HttpSession session,
// @RequestParam注解可以获取到请求参数
// required 可以设置这个参数是否必须,若为必须,但是没有传,则返回400 。有点类似@RequestMapping注解中的params参数
// defaultValue 设置参数的默认值
@RequestParam(value = "username", required = false, defaultValue = "zwc") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password
) {
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
return "ok";
}不使用注解,依靠形参名来接收参数(用的少,可读性比较差)
这个和反射机制有关,只需要在编译的时候使用-parameters 编译即可
之后可以不需要使用 @RequestParam注解来指定参数名称,可以依靠方法的形参名来获取请求参数
<!-- pom.xml中添加如下-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.11.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>17</source>
<target>17</target>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-parameters</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>使用pojo类接收请求参数
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
}
// 使用pojo类来接收请求参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParams1", method = RequestMethod.POST, params = {"username", "password"})
// 参数只要传对应的pojo类即可,spring会调用对应的反射机制给user设置属性
public String testParams1(User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return "ok";
}@RequestHeader注解获取请求头信息
@GetMapping("/requestHeader")
public String testRequestHeader(@RequestHeader(value = "host",defaultValue = "zwc") String host) {
System.out.println(host);
return "ok";
}@CookieValue注解获取cookie
@GetMapping("/getCookie")
public String testGetCookie(@CookieValue(value = "username") String username) {
System.out.println(username);
return "ok";
}解决post乱码问题
使用springmvc内置的过滤器解决post请求乱码问题
<!--web.xml -->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<!--让响应体的编码方式强制使用上述的字符集 -->
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<!-- 让请求体的编码方式强制使用上述的字符集-->
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>解决get请求的乱码问题
<!-- tomcat 的home目录的conf/server.xml中设置URI的编码方式即可 tomcat9和10默认为utf-8 -->
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443"
maxParameterCount="1000"
URIEncoding="UTF-8"
/>三大域对象
Request域
设置request域上面的属性,有四种方法
使用model接口设置request域上面的属性
@GetMapping("/request1")
public String request1(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", "zwc");
return "request";
}使用Map接口设置request域上面的属性
@GetMapping("/request2")
public String request2(Map map) {
map.put("name", "zwc1");
return "request";
}使用ModelMap类设置request域上面的属性
@GetMapping("/request3")
public String request3(ModelMap modelMap) {
modelMap.addAttribute("name", "zwc3");
return "request";
}使用ModelAndView设置request域上面的属性
@GetMapping("/request4")
public ModelAndView request3() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("name", "zwc4");
//设置试图的名称
modelAndView.setViewName("request");
return modelAndView;
}Session域
使用原生的 HttpSession 设置session域上面的属性
@GetMapping("/session1")
public String session1(HttpSession httpSession) {
httpSession.setAttribute("name", "zwc");
return "session";
}使用ModelMap +@SessionAttributes注解设置session域上面的属性
这种方法是可以使用上述设置request域的属性的方法,但是只需要在类上使用@SessionAttributes注解声明哪些属性是session域的即可
@Controller
@SessionAttributes({"name"})
public class Session域共享 {
@GetMapping("/session2")
public String session2(ModelMap modelMap) {
modelMap.addAttribute("name", "zwc2");
return "session";
}
}application域
@Controller
public class application域共享 {
@GetMapping("/application")
public String application(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
ServletContext application = httpServletRequest.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("name", "Zwc");
return "application";
}重定向和转发
// spring mvc中重定向和转发的写法
@GetMapping("/forward")
public String forward() {
System.out.println("hhh");
// 转发到/ok
return "forward:/ok";
}
@GetMapping("/redirect")
public String redirect() {
System.out.println("hhh");
// 转发到/ok
return "redirect:/ok";
}SpringMVC中常用的视图:
InternalResourceView:内部资源视图(SpringMvc内置的,专门负责解析Jsp模版语法的,另外也负责转发forward功能的实现)
RedirectView:重定向视图(是springmvc内置的,专门负责重定向 redirect功能的实现)
ThymeleadfView:Thymeleaf视图(是第三方的,专门负责解析Thymeleaf模版语法的)
实现视图机制的核心类与核心接口
DispatcherServlet:前端控制器
负责接收前端的请求
根据请求路径找到对应的controller的方法
执行controller的方法
返回modelAndView对象
处理视图
ViewResolver接口,视图解析器接口
将逻辑视图名称转化为物理视图名称,并最终返回一个View接口对象
View接口
将模版语法的字符串转化为html代码,并响应给前端(render)
视图控制器 and 注解驱动
若你的某个controller的某个方法只是单纯地跳转视图,没有业务逻辑代码,那么这个方法可以不写
在springmvc.xml配置文件中配置
<!--路径为/ok ,展示的页面为 前缀+ok+后缀-->
<mvc:view-controller path="/ok" view-name="ok"/>
<!-- 配置了上面的,你的注解会失效,需要手动配置开启注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />静态资源处理
<!-- 静态资源的处理-->
<!-- 使用默认的tomcat自带的默认的servlet处理静态资源(推荐)-->
<!-- <mvc:default-servlet-handler/>-->
<!-- 表示/static下面的所有文件 去/static/下面查找-->
<mvc:resources mapping="/static/**" location="/static/"/>
<!-- 使用这两种方式都需要开启注解驱动,否则注解会失效-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>Restful
对请求方法的约束
get 查询
post 新增
put 更新全部字段
patch 更新部分字段
delete 删除
对URL对约束
get请求 : /user/1
delete: /user/1
post : /user
…
使用标准状态码来表示操作结果
200 OK:请求成功。201 Created:资源成功创建。(post请求返回)204 No Content:请求成功,但没有返回内容(通常用于 DELETE 操作)。400 Bad Request:客户端请求无效。401 Unauthorized:未经授权。403 Forbidden:拒绝访问。404 Not Found:资源未找到。500 Internal Server Error:服务器内部错误
ResponseBody注解
这个注解的作用是将控制器方法的返回值直接写入HTTP响应体中,而不是将其解释为一个视图名称(springmvc通过消息转换器将返回值转化为对应的格式)
常见的消息转化器
StringHttpMessageConverter : 将字符串数据转换为 Java 对象,或将 Java 对象转换为字符串数据(默认的消息处理器)
FormHttpMessageConverter:将表单数据(application/x-www-form-urlencoded)转换为 MultiValueMap<String, String>,或将 MultiValueMap<String, String> 转换为表单数据
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter:将 JSON 数据转换为 Java 对象,或将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 数据。
需要安装依赖
xml<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.12.3</version> </dependency>
RestController 注解
这个注解等价于 Controller + ResponseBody ,是一种简化的写法
RequestBody 注解
这个注解只能作用在方法的参数上,将HTTP请求体中的内容绑定到方法参数上,并根据Content-Type的值 利用消息转化器 转化为对应的格式
@PostMapping("/save")
public String saveUser(@RequestBody leftover.pojo.User user) {
System.out.println("hhh");
System.out.println(user);
return "ok";
}RequestEntity类 和 ResponseEntity类
RequestEntity类
RequestEntity类是用来封装请求协议,包括状态行、请求头、请求体等等信息
具体用法
@GetMapping("/request")
// 泛型是请求体的类型
public String requestEntity(RequestEntity<leftover.pojo.User> userRequestEntity) {
System.out.println(userRequestEntity.getMethod());
// 请求体
System.out.println(userRequestEntity.getBody());
// 请求的url
System.out.println(userRequestEntity.getUrl());
// 返回请求体的类型 class leftover.pojo.User
System.out.println(userRequestEntity.getType());
return "ok";
}ResponseEntity类
使用ResponseEntity ,其方法的返回值必须为ResponseEntity类型 ,泛型是响应体的类型
// 使用ResponseEntity定制响应协议 ,其方法的返回值必须为ResponseEntity类型 ,泛型是响应体的类型
@GetMapping("/response")
public ResponseEntity<leftover.pojo.User> response() {
// return ResponseEntity.ok(new leftover.pojo.User("zwc", 100));
return ResponseEntity.status(400).body(null);
}文件上传和下载
文件上传
spring6和spring5的文件上传不一样(这里只介绍spring6的)
在web.xml的DispatcherServlet中配置,可以配置上传文件的限制
<multipart-config>
<!-- 单个文件的最大大小-->
<!-- <max-file-size>10240000000</max-file-size>-->
<!-- 整个表单所有文件上传的最大值-->
<!-- <max-request-size>102400000</max-request-size>-->
<!-- 最小上传文件大小-->
<file-size-threshold>1</file-size-threshold>
</multipart-config> @PostMapping("/upload")
public ResponseEntity<ResponseMessage> upload(@RequestParam("fileName") MultipartFile[] multipartFiles, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) throws IOException {
ResponseMessage responseMessage = new ResponseMessage();
try {
for (MultipartFile multipartFile : multipartFiles) {
// formdata的key 的名称
String name = multipartFile.getName();
System.out.println(name);
// 上传文件的最初的文件名称
String originalFilename = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
InputStream inputStream = multipartFile.getInputStream();
ServletContext application = httpServletRequest.getServletContext();
String realPath = application.getRealPath("/upload");
File uploadDirFile = new File(realPath);
if (!uploadDirFile.exists()) {
uploadDirFile.mkdir();
}
//使用uuid作为文件名
File uploadFile = new File(realPath + File.separator + String.valueOf(UUID.randomUUID()).substring(8) + originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf('.')));
System.out.println("文件的保存位置:" + uploadFile.getAbsolutePath());
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(uploadFile));
bufferedOutputStream.write(inputStream.readAllBytes());
inputStream.close();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
responseMessage.setCode(1);
responseMessage.setMessage("文件上传成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
responseMessage.setCode(0);
responseMessage.setMessage("文件上传失败");
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(responseMessage);
}文件下载
@PostMapping("/download")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> download(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException {
File file = new File(httpServletRequest.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload") + File.separator + "hh.jpg");
//设置请求头
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
//设置contentType 为 application/octet-stream
httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM);
// filename为浏览器默认保存的文件名
// 设置 Content-Disposition 为 form-data; name="attachment"; filename="hh.jpg"
// inline:表示内容应该内联显示(通常用于显示 PDF 或图像)。
//attachment:表示内容应该作为附件下载。
httpHeaders.setContentDispositionFormData("attachment", file.getName());
//body里面返回的是一个字节数组
return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath()), httpHeaders, HttpStatus.OK);
//以inline的形式展示
//设置ContentType为application/pdf
// httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_PDF);
//根据文件的类型动态设置contentType
httpHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.valueOf(Files.probeContentType(file.toPath())));
}自定义异常处理
springmvc中有一个默认的异常处理器,针对一些常见的异常进行了处理,会显示对应的异常消息,同时我们也可以自定义异常处理
可以使用注解方式定义(推荐),也可以使用xml的方式定义(不推荐)
异常处理方法可以返回 ResponseEntity 、ModelAndView ,void 、string 等类型
全局异常处理器
下面这个例子中,所有的ResourceNotFoundException异常都会经过这个处理,最后返回给前端一个ResponseEntity
//@ControllerAdvice 用于全局处理应用程序中的异常
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
// 指定处理哪些异常,若没指定,则以方法的参数为准
// 异常处理方法可以返回 ResponseEntity 、ModelAndView ,void 、string
@ExceptionHandler({ResourceNotFoundException.class})
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> handleResourceNotFoundException(ResourceNotFoundException ex) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error", ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}针对某个Controller的异常处理器
下面这个异常处理器定义在某个Controller中,他只能处理这个Controller中的异常 ,例如这个Controller中如果有 InvalidInputException ,则会经过下面的ExceptionHandler处理
@RestController
public class User {
@ExceptionHandler({InvalidInputException.class})
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> handleInvalidInputException(InvalidInputException ex) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error", ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity getUser(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
if (id > 100)
throw new ResourceNotFoundException("资源没找到");
else if (id < 0) {
throw new InvalidInputException("参数不合法");
} else {
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
}
}拦截器
拦截器的基本配置

<!-- spring-mvc.xml -->
<!-- 这种配置方式默认拦截所有的请求路径-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!-- 第一种配置方式-->
<!-- <bean class="leftover.intercertor.LoggingInterceptor"/>-->
<!-- 第二种配置方式 ,这个拦截器要注册成一个bean(加上Component注解)-->
<ref bean="loggingInterceptor"/>
<!-- 拦截器的高级配置方式(可以设置拦截的路径)-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/secured/**"/>
<!-- <mvc:exclude-mapping path=""/>-->
<ref bean="authInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>拦截器的三个方法
preHandle : 在controller执行之前调用,返回true代表放行,返回false则拦截(这次请求中只要有一个拦截器返回了false,那么这次请求都会被拦截,且后面的拦截器的preHandle方法将不再执行,不过前面的返回true的拦截器的afterCompletion方法会执行)
postHandle:在渲染页面之前、controller方法调用之后执行,且controller没有异常抛出才会执行
afterCompletion: 若这次请求没有被拦截,则所有拦截器的afterCompletion会在渲染页面之后被执行(无论有没有发生异常),
若这次请求被拦截了,则返回false的那个拦截器前面的拦截器的afterCompletion会执行
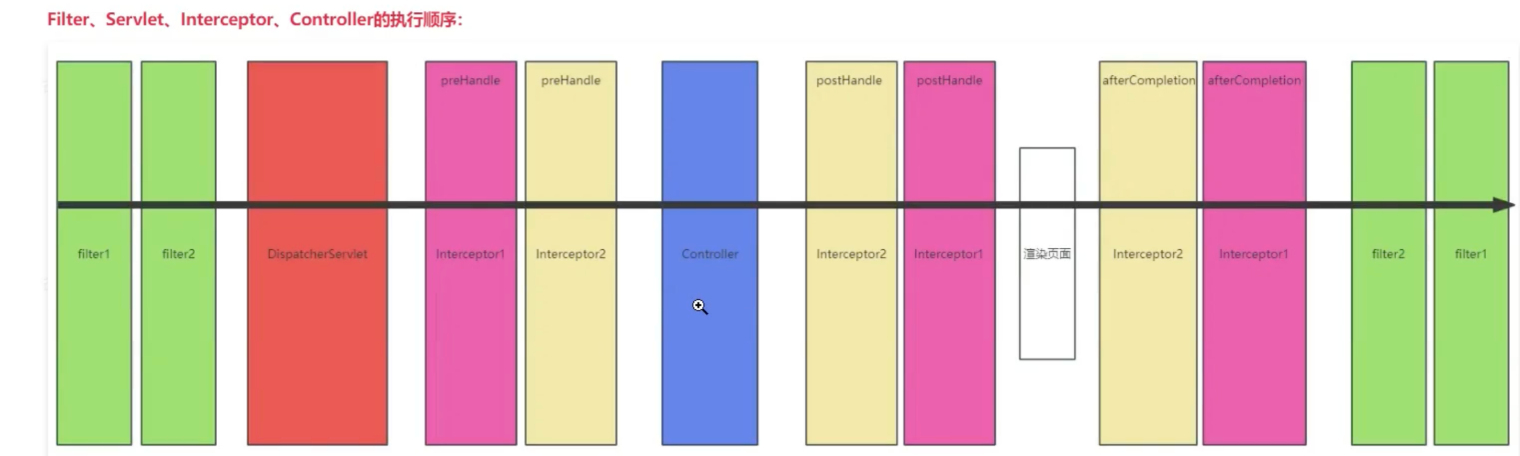
拦截器和过滤器的区别
拦截器
- 拦截器是 Spring MVC 框架的一部分,因此它们在 Spring MVC 层次上工作。
- 拦截器仅适用于处理经过 Spring MVC DispatcherServlet 的请求。
- 拦截器主要用于预处理和后处理Controller方法的调用。
- 适合特定于业务逻辑的任务,例如权限检查、用户跟踪、事务管理等。
- 仅用于 Spring MVC 应用中。
过滤器
过滤器是 Java Servlet 规范的一部分,因此它们在 Servlet 容器级别工作。
过滤器可以用于所有进入应用程序的请求,不限于 Spring MVC 应用。
适合全局性、通用性的任务,例如安全、日志记录、编码设置、跨域资源共享(CORS)等。
可用于非 Spring MVC 应用或混合应用。
过滤器 更适合全局性、通用性的任务,而拦截器**更适合与业务逻辑相关的任务。
全注解开发
⚠️若使用全注解开发,则不需要配置web.xml的位置(在idea中配置了web.xml的位置则会使用web.xml),不过要配置资源的根路径
总的配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("leftover")
public class WebConfigInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
/**
* spring的配置
*
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[0];
}
/**
* springmvc的配置
*
* @return
*/
//加载springmvc的配置文件
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
/**
* 配置 DispatcherServlet 的url-pattern
*
* @return
*/
// 配置 DispatcherServlet 的url-pattern
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
}springmvc的配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("leftover")
//开启mvc的注解驱动
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
// 配置视图处理器
@Bean
public ThymeleafViewResolver getViewResolve(@Qualifier("templateEngine") SpringTemplateEngine springTemplateEngine) {
ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver();
viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
viewResolver.setOrder(1);
viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(springTemplateEngine);
return viewResolver;
}
@Bean("templateEngine")
public SpringTemplateEngine getTemplateEngine(@Qualifier("templateResolver") ITemplateResolver iTemplateResolver) {
SpringTemplateEngine springTemplateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
springTemplateEngine.setTemplateResolver(iTemplateResolver);
return springTemplateEngine;
}
@Bean("templateResolver")
public ITemplateResolver getTemplateResolver(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
SpringResourceTemplateResolver resolver = new SpringResourceTemplateResolver();
resolver.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
resolver.setSuffix(".html");
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/");
resolver.setTemplateMode("HTML");
resolver.setCacheable(false);
resolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
return resolver;
}
// // 开启默认的servlet,可以对静态资源进行处理
// @Override
// public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
// configurer.enable();
// }
// 添加视图控制器
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
// 添加拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
LoggingInterceptor loggingInterceptor = new LoggingInterceptor();
AuthInterceptor authInterceptor = new AuthInterceptor();
registry.addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor);
registry.addInterceptor(authInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/secured/**");
}
// 对一些静态资源处理
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("/static/");
}
}整合ssm
见springmvc项目的restfulUser模块的leftover.config包